Bookkeeping refers to the process of regularly tracking and recording the financial data of a business in the books of accounts. Bookkeeping is an essential responsibility when running a business, it is virtually impossible to run a business without a proper bookkeeping system in place.
A bookkeeper is a person responsible for managing a business’ bookkeeping. It is important to remember that a bookkeeper is not an accountant and, therefore, does not require any certification to perform bookkeeping tasks. In fact, many small business owners tend to take on the role of bookkeeper alongside other responsibilities. Bookkeeping is a very sensitive responsibility, as it involves the disclosure of a business’s financial data. Therefore, bookkeepers are held under strict scrutiny by entrepreneurs, and choosing the right person for the job is paramount for the business’ success.
Why is bookkeeping important?

Bookkeeping is extremely important because it allows an entrepreneur to keep a strict eye on the business’ day to day activity and have all the financial data associated with the business in writing. Having a formal and historic record of the business’ financial activity maximizes transparency and is necessary to prove the business’ financial legitimacy in an audit. Bookkeeping also helps manage the business’ finances efficiently and optimize money spending.
Alongside maintaining the books of accounts, bookkeepers also perform some additional duties that are equally as important for the business. The responsibilities of a bookkeeper include:
- Bookkeeping
- Compiling financial statements
- Tax and audit preparation
- Charting Accounts
Bookkeeping
The primary role of a bookkeeper is the regular tracking and recording of a business’ financial data. This includes all transactions that the business performs on a day-to-day basis. The data is collected in the general ledger in the form of debits and credits, or in layman terms, income and expenses. Bookkeepers are also responsible for processing invoices, whether it be for the business’ accounts payable or receivable. There are two standard systems used for bookkeeping i.e., the single-entry method and the double entry method.
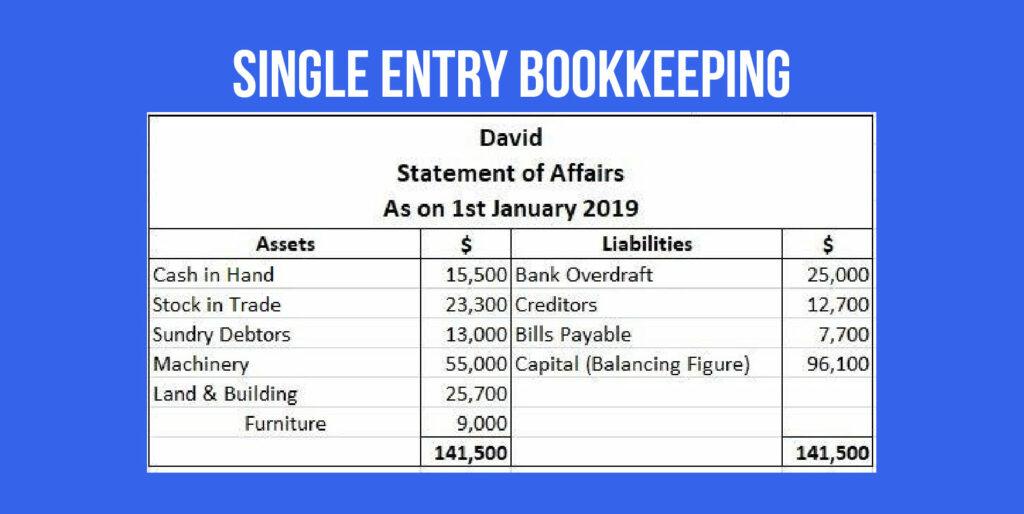
Single-entry bookkeeping
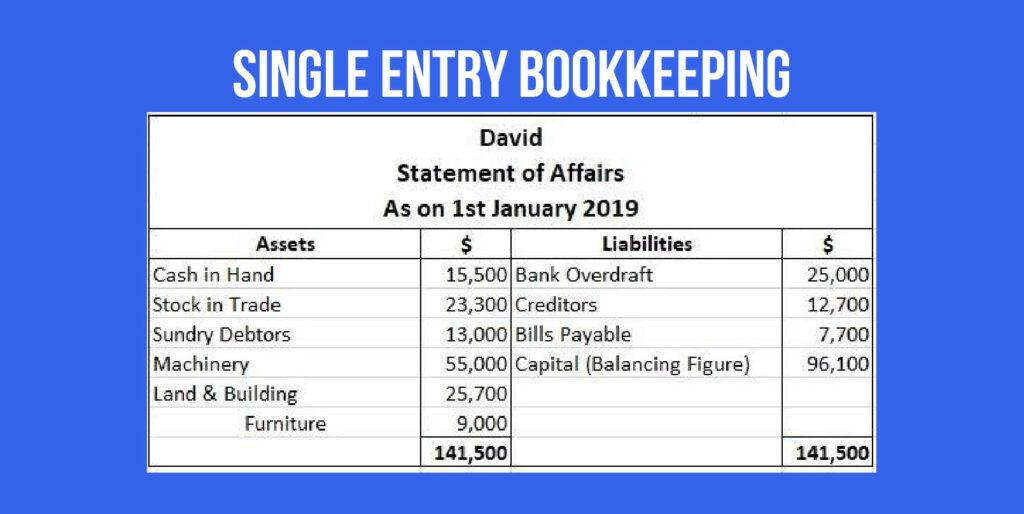
Single-entry or cash-based bookkeeping records transactions once as either debit or credit in the cash book. A general ledger is not maintained in this bookkeeping system.
For example, a business buys inventory worth $5000. Under the single-entry system, this would simply be recorded as a credit of $5000 from the business’ cash.
Double-entry bookkeeping
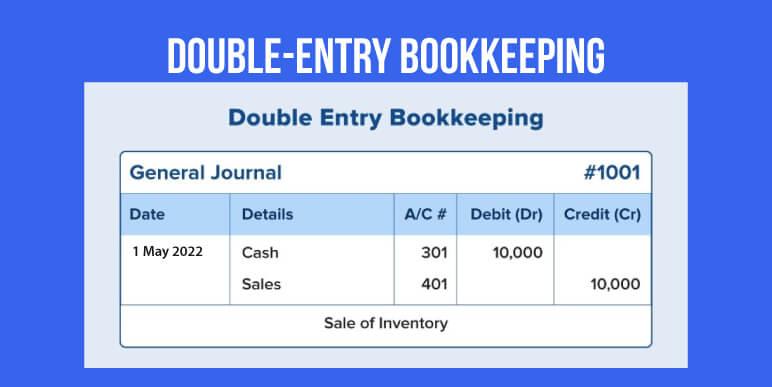
Double entry accounting refers to the concept of each single transaction being reported through a dual effect in the books of accounts.
For example, a business buy’s inventory worth $5000. This would be recorded as a cash credit of $5000, but also as a debit for the business’ inventory value. Essentially, the business’ cash decreases while the business’ inventory value proportionally increases. This system provides a full view of the business’ transactions, highlighting exactly where the money is coming and going and can be used to generate financial statements. The double-entry system is the standard system most businesses operate under today.
Compiling financial statements
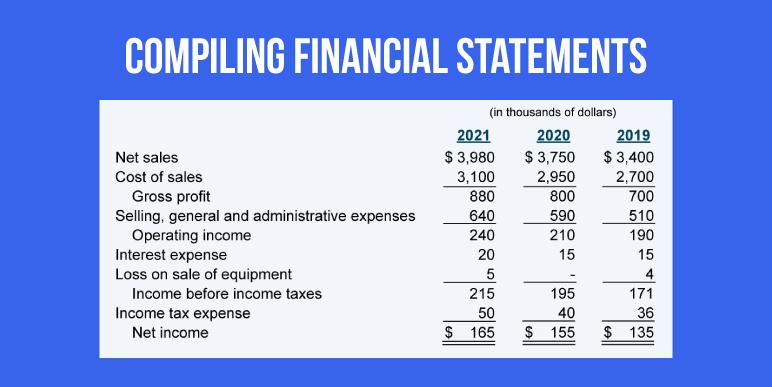
The data recorded in the general ledger by a bookkeeper can be converted into meaningful information in the form of financial statements. Financial statements are a record of the business’ financial information, such as assets, liabilities, equity etc. over a period of time. financial statements can be used to evaluate a business’ performance and financial health, as well as help in decision-making. The three most relevant financial statements are:
The balance sheet
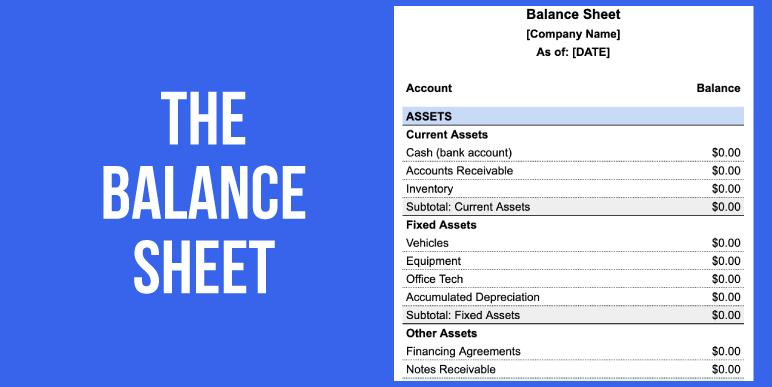
the balance sheet shows data on assets, liabilities, and shareholder’s equity in the form of the accounting equation:
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
The income statement
Corporate Finance Institute describes the income statement as follows: “the Income Statement is one of a company’s core financial statements that shows their profit and loss over a period of time. The profit or loss is determined by taking all revenues and subtracting all expenses from both operating and non-operating activities.”
The cash flow statement

As the name suggests, the cash flow statement tracks and records the flow of cash through the business in the form of earnings and expenses. The purpose of the cash flow statement is to assess the flow of cash through the business over a period of time.
For entrepreneurs looking to learn more about financial statements, Expertise accelerated publication “The guide to the four basic financial statements” provides an in-depth guide to financial statements for beginners.
Tax and audit preparation
Taxes and audits are inevitable over the course of business, and a bookkeeper plays a very important role in preparation of these inevitabilities. By maintaining a precise record of business expenses, salaries, write-offs etc., a bookkeeper lays the groundwork for tax season throughout the year. Equipped with this detailed and precise record, tax filing becomes far less tedious and stressful. Similarly, audits also require a business to have its books of accounts in order. The goal of a financial audit is to ensure transparency in the business’ financial reporting, and any errors in bookkeeping can incur penalties for the business. Having a bookkeeper who can dedicate time to looking over the business’ financial data and ensuring that everything is in order for the audit can be a source of great relief to any entrepreneur. Not having a bookkeeper for tax and audit preparation can leave the business vulnerable to penalties as well as cause great stress when the time for either draws near.
Charting Accounts
A bookkeeper is responsible for maintaining or “charting” a business’ chart of accounts. According to bench publication “What is a Chart of Accounts? A How-To with Examples“, “a chart of accounts is a list of all your company’s “accounts,” together in one place. It provides you with a bird’s eye view of every area of your business that spends or makes money. The main account types include Revenue, Expenses, Assets, Liabilities, and Equity.”
Furthermore, the chart of accounts differs from business to business depending on the daily costs of operations. It is also important to note that a chart of accounts is only used under the double-entry system of bookkeeping.
Charting accounts is very important for financial health evaluation. By categorizing transactions on the basis of regular costs, a more accurate picture is drawn of the business’ performance. It allows for the pinpointing of where and why expenses occurred, and income was received.
When should a business hire a bookkeeper?
Ideally, a business should have a bookkeeper on the team from the start so that everything is properly recorded, and entrepreneurs have the freedom to focus on building the business. Realistically, this is impossible in today’s business climate, and most entrepreneurs have to take the responsibility when starting out. While there is no clear answer to when exactly is the right time to hire a bookkeeper, a smart time to consider the idea is when the business is scaling. This is because entrepreneurs will have to manage a great deal more work when the business scales, and the bookkeeping can end up low on the priority list.
When it comes to hiring a bookkeeper, there are many options available today. A business can opt to hire a part-time or a full-time in-house bookkeeper, or they can try out some of the newer options that the internet and cloud accounting provides in the form of staff augmentation and outsourcing firms.
Expertise Accelerated as your bookkeeping facilitator
Expertise Accelerated (EA) is a Connecticut-based outsourcing and staff augmentation specialist for accounting & finance services. EA is committed to delivering 60 percent quality-assured payroll savings to its US clients.
EA’s service methodology is quality-centric, and this reflects in its rigorous recruitment processes and the US CPA team training the offshore remote professionals for client-specific roles so they become a strategic fit for the client company.
Expertise Accelerated’s bookkeeping services can help US SMEs achieve efficiency and value in their business operations.