In general accounting, Accrual and cash accounting are two methods of recording and recognizing income and expenses in accounting. Each method shapes finances in very different ways.
- Cash accounting records revenues when cash is actually received and expenses when they are actually paid.
- Accrual accounting records revenues when they are earned and expenses when they are incurred, regardless of when cash changes hands.
In short, there two different methods of accounting for business transactions.
This guide covers
- How accrual and cash accounting work.
- How transactions are recorded under both the methods and
- The key differences between the two
What Is Accrual Accounting?
Accrual accounting logs income when earned and expenses when incurred, not when paid. Recognized under the US GAAP, this method shows a clearer picture than cash accounting, which only records money when paid or received.
| If the business earned $20,000 this month, why do we only have $7,000 in the bank? Did something go wrong? |
The accrual accounting method is useful for businesses with credit sales and large inventory. It is more complex than cash accounting but it helps companies plan better and show the full financial health of a company.
What is the revenue threshold for accrual basis accounting?
In the U.S., the IRS generally requires businesses to use the accrual method if they are considered “large” for tax purposes. Businesses are considered large when their average gross receipts threshold* exceeds $30 million.
*Many people confuse gross receipts with revenue. They are similar but gross receipts is a more broad term:
Revenue = sales income
Gross receipts = revenue + other business income sources
When should small businesses have to use an accrual method of accounting in the US?
According the IRS publication, a small business* must use an accrual method if they are keeping an inventory. Cost of goods sold includes inventory. We have to value inventory using the accrual accounting method.
A business qualifies as a small business if its average annual gross receipts are $30 million or less for the prior 3 tax years.
What Is Cash Accounting?
In cash accounting, businesses record money only when they get or spend it. Income is recorded when money comes in, and expenses when money goes out. This method is simple and shows how much money a business actually has on hand. It is especially preferable if a business has less to no inventory.
Cash accounting is simple but it may not be as accurate as the accrual method. It doesn’t show money owed or future expenses, which can make it harder for bigger businesses to track their true financial position. That’s why big companies must use accrual accounting, but small businesses can choose cash or accrual.
For e.g, the business records the January electricity bill in February when it pays it. With accrual accounting, the business records the same bill as an expense in January because it is due then, even though it will pay it in February.
How Cash vs. Accrual Accounting Can Affect Your Business
The accounting method you choose can affect your business finances.
Let’s learn the difference between the two accounting methods with the help of an example.
Clean My House LLC is a company providing residential cleaning services. The company provided cleaning services of $6000 to a client on 20th December 2025. The client paid for the services on 7th January 2025.
Transaction
Service provided: $6,000
Service date: December 20, 2025
Cash received: January 7, 2026
Accrual Accounting Example
(Revenue is recorded when earned, even if cash comes later.)
On Dec 20, 2025 (service performed):
Dr Accounts Receivable 6,000
Cr Service Revenue 6,000
On Jan 7, 2026 (cash collected):
Dr Cash 6,000
Cr Accounts Receivable 6,000
- Revenue is shown in December 2025 (when services were provided).
- Cash is shown in January 2026, but income is already recognized.
Cash Accounting Example
(Revenue is recorded only when cash is received.)
On Dec 20, 2025 (service performed):
No entry will be recorded
On Jan 7, 2026 (cash received):
Dr Cash 6,000
Cr Service Revenue 6,000
- Revenue is shown in January 2026, when cash was received.
- No revenue appears in December under cash accounting.
So, under accrual the $6,000 boosts December’s income, while under cash it shows up in January. That’s why the accrual accounting method is preferred because it recognizes the revenue when it is earned.
Taxes and Accounting Methods
One main difference is when you record income and expenses for taxes.
- Cash Accounting: You only pay taxes on the money you actually get. For example, If you send an invoice in December 2025 but get paid in January 2026, you record that income in 2026 (when you have received cash).
- Accrual Accounting: You pay taxes on income when you earn it. Using the same example, the $6,000 invoice would count as 2025 income even if the payment arrives in January 2026.
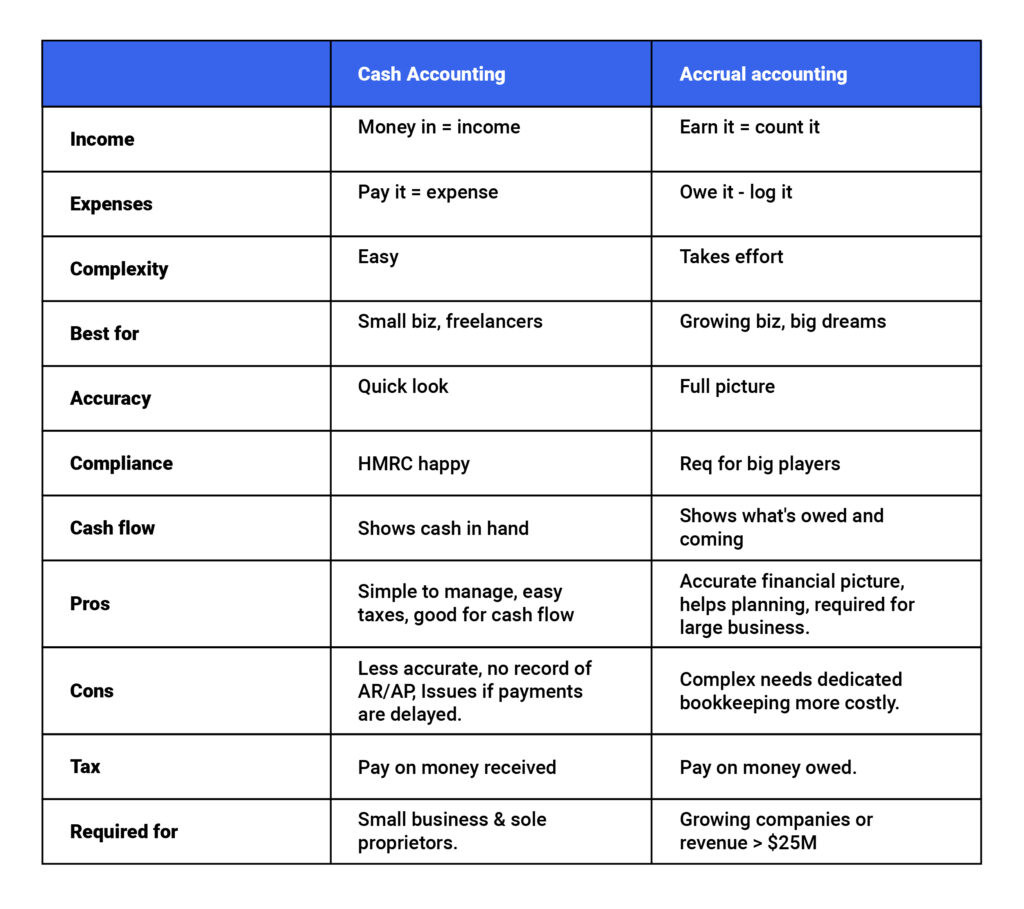
Comparison Table (Cash vs Accrual)
Accounting Software Options
Many accounting software platforms allow you to choose either method:
-
QuickBooks:
Lets you pick cash or accrual and run reports for either.
-
Wave:
Uses accrual by default but allows switching to cash.
-
Bench:
Offers cash, modified cash, and accrual options. Modified cash helps track inventory and long-term assets, like accrual accounting.
Choosing between cash and accrual accounting is important, but you don’t have to decide alone. EA’s certified accountants, experienced in QuickBooks, Xero and Zoho, are here to guide you and manage your books with confidence.
What’s Best for Your Business?
Here are the key factors to decide which accounting method fits your business:
- Business Size – Small businesses often use cash accounting; larger ones must use accrual.
- Revenue Level – If yearly revenue is over $30 million, the IRS requires accrual accounting.
- Inventory – Businesses with large inventories usually need accrual for accurate tracking.
- Growth Plans – Companies planning to scale may enjoy accrual early to avoid switching later.
- Cash Flow Needs – Cash accounting shows actual cash in hand, helpful for small firms with limited funds.
- Compliance – Public companies and corporations must follow accrual under GAAP rules.
Small Businesses and Accrual Accounting
While accrual accounting seems like the best option for any business in the long-run, small business owners do not opt for it, mainly because of the extra cost associated with the process.
The cost of a dedicated bookkeeper is often too high, while not hiring one leads to process inefficiency. Fortunately, there is an easy solution to this conundrum: Staff augmentation.
Staff augmentation refers to hiring manhours and/or expertise from a third-party service provider to enhance capacity. Many small businesses today leverage staff augmentation services as an instrument to step up their competitive strength.
When it comes to staff augmentation services, accounting is one of the most popular choices. EA publication “Why staff augmentation is vital for US companies?” elaborates the significance of staff augmentation for US companies in the prevailing business context.
Leveraging EA’s staff augmentation services for your accruals-based accounting needs means you will have accounting and finance professionals at your disposal at 40 percent of the US cost.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between Accrual vs cash accounting helps you choose the right method for your business. If you are starting out, cash accounting is usually the best choice. For businesses that manage stock or inventory, accrual accounting works better.
Still unsure which accounting method is right for your business? Our team is here to help, talk to us today.
FAQs
1. What accounting method should a growing business use?
If you expect your business to grow, accrual accounting may be the better choice. Small businesses can outgrow cash accounting.
Switching to accrual later takes time and can be tricky. Starting with accrual accounting early can save you time and effort. It helps as your business expands. It is especially useful if you expect higher revenue or a larger client base.
2.How do I switch from cash to accrual accounting?
If your business grows and you need to switch accounting methods, you must adjust your books first.
Add prepaid expenses, accrued expenses and accounts receivable. Then subtract cash payments, customer prepayments, and cash receipts.
After you make these adjustments, file Form 3115 with the IRS. Attach your profit and loss statements. Add your balance sheets. Include any adjustments from the previous year when you submit the form.
3.What factors should I look at when I choose an accounting method?
Every business is different. You need to think about legal rules and your business size. Also, consider your growth plans and future accounting needs.
Look at the types of transactions you handle. Finally, check what accounts you need. Choosing the right accounting method early makes bookkeeping simple. It also keeps your finances organized as your business grows.
4.Can a business switch from accrual to cash accounting?
Yes, a business can switch from accrual accounting to cash accounting when reporting income on its tax return. To do this, the company must adjust its books to reflect the change in accounting method. This includes adding accounts receivable and payable, and tracking prepaid and accrued expenses. It also covers updating records of cash payments and receipts.
The business must also prepare a statement showing how income and expenses differ between the two methods. The company must file Form 3115 with the IRS. They also need to attach a statement, profit and loss reports, balance sheets, and any adjustments from the past year.
5. What is a hybrid accounting method?
As an entrepreneur, you might wish you could combine the simplicity of cash accounting with the accuracy of accrual—the best of both worlds. The good news is, there’s a third option: hybrid accounting, which blends elements of both methods.

