Imagine you’re about to outsource a critical business function i.e. your accounts payable. You rush to pick a vendor, skip clarifying deliverables, and later face cost overruns, process misalignments, or compliance gaps. That’s what happens when you bypass a proper RFP process.
The RFP process is not just paperwork; it’s your playbook to solicit competitive, compliant, transparent proposals and choose a partner who really fits. In this post, we’ll explore the request for proposal RFP process, walk through RFP process steps, and share how to improve the RFP process especially in AP outsourcing.
Key Takeaways
- Understand what RFP process is and why it matters
- Learn the RFP process steps in detail
- See exactly how the RFP process supports AP outsourcing
- Get best practices to improve RFP process and avoid common pitfalls
What Is the RFP Process?
Request for Proposal (RFP) is an official request where an organization requests potential vendors to prepare specific plans to provide a specified amount of work. The RFP process refers to the series of actions, i.e. defining requirements for the contract award, which will make sure that you can compare the proposals of the vendors objectively and make a sound decision.
In short, the RFP process is your procurement model: identify need, solicit proposals, make decisions, and recruit. In the private market or in the state that regulates procurement, the RFP process introduces order, justice, and clarity in selecting the vendors.
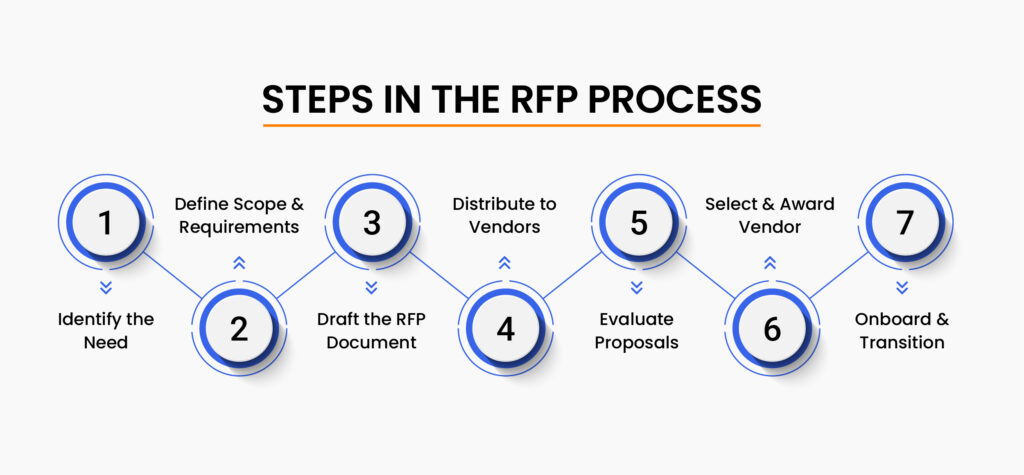
Steps in the RFP Process
RFPs are a backbone of U.S. procurement, especially in the public sector. The RFP process is often not optional in U.S. public procurement, it’s required by law, policy, and good governance. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the RFP process:
| Step | Purpose / Output | Key Participants |
| 1. Identify the Need | Define what services or functions need to be outsourced or procured by assessing business gaps, priorities, and budget. | Leadership, Operations, Finance |
| 2. Define Scope & Requirements | Clearly outline the project scope, deliverables, and exclusions to ensure vendors understand expectations. | Procurement Team, Business Stakeholders |
| 3. Draft the RFP Document | Develop a detailed RFP that includes requirements, evaluation criteria, deliverables, and timelines. | Procurement, Legal, Subject Matter Experts |
| 4. Distribute to Vendors | Share the RFP with qualified vendors, handle queries transparently, and ensure equal communication. | Procurement, Vendor Relations |
| 5. Evaluate Proposals | Review and score vendor submissions based on technical, financial, and strategic alignment. | Cross-Functional Evaluation Team |
| 6. Select & Award Vendor | Choose the most suitable vendor, negotiate final terms, and execute the contract. | Procurement, Legal, Senior Management |
| 7. Onboard & Transition | Manage changeover and transfer operations to the selected vendor for seamless implementation. | Project Management, Operations, Vendor |
Notes:
- Define milestones and deadlines within each step to maintain momentum.
- Use a weighted scoring matrix (for example, price 30%, technical capability 40%, service 30%) to bring objectivity.
- Publish addenda if clarifications or changes occur after distributing the RFP.
Importance of the RFP Process in the United States
RFPs are a backbone of U.S. procurement—especially in the public sector. In Fiscal Year 2023, the U.S. federal government obligated about $759 billion in contracts. U.S. Government Accountability Office
Some reasons RFPs are crucial in the U.S.:
- Agencies must comply with the Competition in Contracting Act (CICA) and follow Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) frameworks to maintain fairness and transparency.
- Many states centralize procurement, giving central bodies authority over non-IT contracts.
- RFPs provide audit trails, transparency, competition, and accountability—especially critical when public funds are involved.
In effect, the RFP process is often not optional in U.S. public procurement—it’s required by law, policy, and good governance.
RFP Process in Accounts Payable Outsourcing
Now, let’s map how the request for proposal RFP process strengthens an AP outsourcing initiative, using your checklist as the backbone:
- Defines Scope Clearly
A strong RFP spells out exactly which AP tasks are included—invoice capture, 3-way matching, vendor support, payments. That clarity prevents scope creeping and sets mutual expectations.
- Drives Competitive Pricing
Inviting multiple proposals allows you to benchmark cost models (e.g. per transaction, FTE, hybrid). You gain pricing leverage while preserving service quality.
- Evaluates Technology Capabilities
Require vendors to demonstrate automation, OCR/RPA, ERP integration, and digital dashboards. This ensures your AP function evolves from manual to modern.
- Strengthens Compliance & Controls
Ask vendors to illustrate fraud prevention, audit trails, SOX/IFRS compliance readiness. You protect yourself from regulatory, financial, and reputational risk.
- Improves Vendor Relationship Management
Your RFP should request details on vendor onboarding, query resolution, and SLA escalation. That fosters long-term supplier satisfaction and supports Vendor Management as a Service (VMaaS).
- Supports Cash Flow Optimization
Vendors should propose strategies for Days Payable Outstanding (DPO), early-payment discounts, and payment terms. Now your AP outsourcing is also a cash optimization lever.
- Builds Accountability via SLAs & KPIs
Define measurable metrics, cycle times, percentage of touchless invoices, and query resolution time. This holds your partner performance driven.
- Ensures Smooth Transition & Change Management
Require a transition roadmap and onboarding plan. This minimizes disruption when shifting operations offshore or nearshore.
- Strengthens Reconciliation & Reporting
Ensure your RFP covers reconciliation accuracy, timely month-end closes, and real-time reporting for better financial visibility.
- Incorporates Risk Management & Business Continuity
Require vendors to outline data security, redundancy, and disaster recovery plans to keep AP operations resilient.
Note: Without a properly structured RFP, AP outsourcing often becomes fragmented, misaligned, and risky.
Best Practices for Managing an RFP
Here are actionable tips to improve RFP process and get better outcomes:
A well-executed RFP process not only ensures fairness and compliance but also drives better value, stronger vendor relationships, and more strategic outcomes. By applying the following practical tips, organizations can enhance efficiency, consistency, and transparency throughout their procurement cycle.
- Publish evaluation criteria transparently in your RFP so vendors know exactly how they’ll be judged.
- Engage cross-functional stakeholders early (finance, IT, operations, legal) to build alignment.
- Stick to defined requirements; if changes are needed, issue addenda rather than ad hoc edits.
- Host vendor Q&A sessions to clarify terms and equalize information access
- Use weighted scoring matrices to avoid subjective bias.
- Leverage RFP software / response platforms to streamline comparisons, tracking, and version control. According to Loopio, 65% of teams now use RFP response software, up from 48% previously.
- Run mock evaluations in advance to test your scoring thresholds
- Communicate clearly and promptly—share timelines, answer questions, and update vendors.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Unclear or overly broad scope → vendors bid wildly diverging solutions
- Frequent requirement changes mid-process → confusion, unfair advantage
- Focusing too much on lowest prices → compromising quality or reliability
- Ignoring vendor track records or references
- Omitting SLA / KPI definitions → no accountability
- Neglecting compliance or audit controls → risk exposure
- Weak or delayed transition planning → business disruption
Conclusion
The RFP process is more than a procurement ritual; it’s a strategic tool for precise vendors. It is a strategic instrument for accurate selection of vendors, reduction of risks, and value creation. RFP in AP outsourcing provides scope of transparency, cost competitiveness, tech capability validation, enhances compliance, vendor relationship, cash flow support and accountability.
By taking steps of the RFP process in a systematic manner, best practices to enhance the rfp process, and avoiding some of the most common pitfalls, your RFP is a differentiator, rather than a burden.

